HEPA and ULPA filters are high-efficiency air filters designed to trap tiny particles. HEPA filters capture at least 99.97% of particles 0.3 microns or larger, making them suitable for most environments like homes and hospitals. ULPA filters offer even higher efficiency, trapping 99.999% of particles down to 0.12 microns, ideal for ultra-clean spaces such as labs and semiconductor manufacturing. Understanding their differences can help you choose the right filter—more details are just a step away.
Key Takeaways
- HEPA filters remove ≥99.97% of particles ≥0.3 microns, while ULPA filters trap ≥99.999% of particles down to 0.12 microns.
- ULPA filters offer higher filtration efficiency for ultra-fine particles but are more expensive and have increased maintenance needs.
- HEPA filters are suitable for general environments like homes, hospitals, and laboratories; ULPA filters are used in ultra-clean settings like semiconductor manufacturing.
- ULPA filters have higher airflow resistance and costs, making them less practical for everyday use compared to HEPA filters.
- Certification standards verify filter performance: HEPA traps ≥99.97% of 0.3-micron particles; ULPA traps ≥99.999% of 0.12-micron particles.
What Are HEPA and ULPA Filters?

Have you ever wondered how certain environments stay so clean and free of harmful particles? HEPA and ULPA filters are key to that cleanliness. HEPA, or High-Efficiency Particulate Air filters, capture at least 99.97% of particles as small as 0.3 microns. They’re common in homes, hospitals, and labs. ULPA, or Ultra-Low Particulate Air filters, go even further, trapping 99.999% of particles down to 0.12 microns. These filters use dense fiber mats to trap particles through diffusion, interception, and impaction. Both types are made from high-quality materials, designed to remove contaminants from the air effectively. Their primary purpose is to improve air quality and protect health by filtering out dust, allergens, bacteria, and other microscopic particles. Additionally, understanding the tuning of these filters can help optimize their performance for specific environments.
How Do HEPA and ULPA Filters Work?

HEPA and ULPA filters work by trapping airborne particles as air passes through their dense fiber matrices. When air flows through, the filters capture particles via several mechanisms. You benefit from this filtration process by reducing contaminants in your environment. The key mechanisms include:
HEPA and ULPA filters trap airborne particles through multiple mechanisms, ensuring cleaner, safer environments.
- Interception: particles follow airflow lines and stick to fibers when close enough.
- Impaction: larger particles collide with fibers directly due to inertia.
- Diffusion: very small particles move randomly and eventually hit fibers.
- Sieving: particles larger than the pore size are physically blocked.
- Electrostatic attraction: static charges draw particles toward fibers.
This combination guarantees effective removal of particles, making these filters essential for maintaining clean air in sensitive environments.
Filtration Efficiency and Particle Sizes

Filtration efficiency of HEPA and ULPA filters varies depending on the size of the particles they can remove. HEPA filters typically capture at least 99.97% of particles as small as 0.3 microns, making them effective against common airborne contaminants like dust, pollen, and bacteria. ULPA filters, on the other hand, achieve even higher efficiency—removing 99.999% of particles down to 0.12 microns—targeting ultrafine particles, viruses, and airborne toxins. The key difference lies in their ability to trap smaller particles more effectively. As particle size decreases, filtration becomes more challenging, requiring finer filter media. Your choice between HEPA and ULPA depends on the level of cleanliness you need and the specific particle sizes you aim to remove from the environment. Additionally, filter media quality plays a crucial role in determining overall filtration performance.
Materials Used in HEPA and ULPA Filters

Both HEPA and ULPA filters rely on specialized filter media composed of densely packed fibers, typically made from materials like fiberglass, polypropylene, or pleated cellulose. These materials are chosen for their durability, electrostatic properties, and fine fiber structure, which trap microscopic particles effectively. The fibers are arranged in a dense matrix to maximize surface area and filtration efficiency. Additionally, some filter media incorporate antimicrobial properties to inhibit microbial growth and improve air quality. Understanding the materials helps you appreciate their performance:
- Fiberglass: Offers high filtration efficiency and thermal resistance.
- Polypropylene: Lightweight, chemical-resistant, and easy to mold into pleats.
- Pleated cellulose: Cost-effective with good filtration capabilities.
- Electrostatic properties: Some materials can hold an electric charge to attract particles.
- Durability: Ensures filters maintain performance over time.
Applications and Industries for HEPA Filters

Have you ever wondered where HEPA filters are most essential? You’ll find them in hospitals, cleanrooms, and laboratories, where maintaining sterile environments is critical. They’re also common in manufacturing plants that produce electronics, pharmaceuticals, and aerospace components. In healthcare, HEPA filters trap airborne bacteria, viruses, and dust, protecting patients and staff. In cleanrooms, they ensure products meet strict quality standards by filtering out even microscopic particles. You’ll also see them in HVAC systems to improve indoor air quality in homes, offices, and airports. Their ability to remove at least 99.97% of particles as small as 0.3 microns makes them indispensable for environments requiring high purity and safety. If you work or live in these settings, HEPA filters play a crucial role in safeguarding health and product integrity. High-efficiency filtration is a key feature that makes HEPA filters suitable for these demanding applications.
When to Use ULPA Filters

ULPA filters are ideal when you need the highest level of airborne particle removal, especially in environments where even microscopic contamination can cause significant issues. Use ULPA filters in settings like semiconductor manufacturing, pharmaceutical cleanrooms, or aerospace laboratories that demand near-total particle elimination. They’re essential when dealing with:
- Ultrafine particles smaller than 0.1 microns
- Contamination-sensitive research
- High-risk medical environments
- Sterile pharmaceutical production
- Precision manufacturing processes
If your application involves strict contamination control or requires the removal of particles invisible to the naked eye, ULPA filters are the right choice. They ensure the cleanest environment possible, reducing the risk of product failure or contamination-related hazards. When selecting filtration systems, consider the filter efficiency to guarantee maximum performance. Opt for ULPA filters when nothing but the highest purity will do.
Comparing Cost and Maintenance

When comparing HEPA and ULPA filters, you’ll notice differences in initial costs and ongoing expenses. ULPA filters often come with higher purchase prices but may require less frequent replacements, affecting long-term maintenance. Understanding these cost points helps you choose the best option for your budget and needs. Additionally, considering the best filter types for specific environments can optimize both performance and savings over time.
Initial Purchase Expenses
HEPA filters generally come with a lower initial purchase price compared to ULPA filters, making them more attractive for budgets-conscious buyers. This cost difference reflects their simpler design and less advanced filtration capabilities. When considering upfront expenses, you’ll find that HEPA units are more affordable initially. Keep in mind, however, that ULPA filters, while pricier upfront, often justify the cost with higher performance in specialized environments. To help you compare, here are some key points:
- HEPA filters are typically 30-50% cheaper upfront
- ULPA filters require more robust housing and installation
- Initial costs depend on filter size and capacity
- Budget constraints favor HEPA filters for general use
- ULPA filters are more common in niche, high-purity settings
- Filtration efficiency varies significantly between HEPA and ULPA filters, impacting their suitability for different environments
Choosing the right filter depends on your specific needs and budget.
Long-term Upkeep Costs
While initial purchase price is an important factor, long-term upkeep costs can considerably influence the overall affordability of your air filtration system. HEPA filters generally have lower maintenance costs because they last longer and are easier to clean or replace. ULPA filters, on the other hand, tend to be more expensive over time due to their specialized construction and higher replacement costs. You’ll also need to factor in energy consumption; ULPA filters often require more power to operate efficiently, increasing your utility bills. Additionally, routine inspections and occasional repairs can add up, especially if you choose high-end filters with complex designs. Moreover, understanding filter lifespan and replacement intervals can help you better anticipate ongoing expenses. Overall, understanding these ongoing expenses helps you make a smarter decision that balances initial costs with long-term financial sustainability.
Replacement Frequency
The frequency with which you need to replace HEPA and ULPA filters directly impacts your ongoing maintenance costs. HEPA filters typically last between 6 to 12 months, depending on usage and environment, while ULPA filters often need replacement every 12 to 18 months. Knowing this helps you plan budgets and avoid unexpected expenses. Proper track development in filter design can also influence longevity and performance. Consider these factors: – Filtration efficiency: Higher efficiency may reduce lifespan. – Air quality levels: Dirtier environments demand more frequent changes. – Usage intensity: Heavy-duty use shortens replacement intervals. – Maintenance routines: Regular inspections can extend filter life. – Cost differences: ULPA filters usually cost more upfront, affecting replacement budgets. Understanding these points enables you to manage costs effectively and maintain ideal filtration performance.
Advantages and Limitations of Each Filter Type
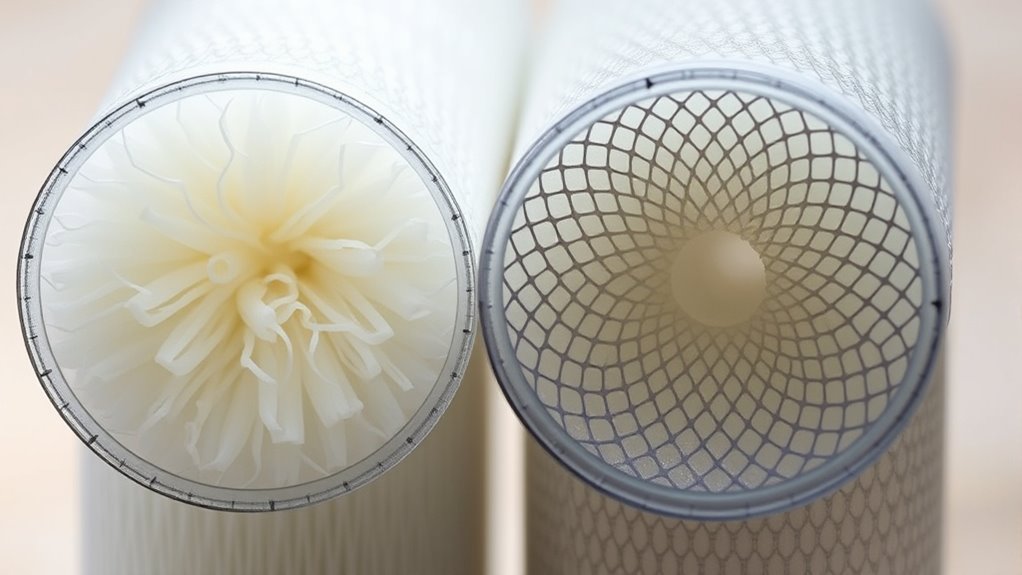
Both HEPA and ULPA filters offer distinct advantages that make them suitable for different filtration needs, but each also has limitations to contemplate. HEPA filters excel at removing airborne particles down to 0.3 microns, making them efficient and cost-effective for most environments. ULPA filters, on the other hand, trap particles as small as 0.1 microns, providing superior purification for sensitive settings. However, ULPA filters tend to be more expensive and require more maintenance. Consider the following comparison: filter efficiency is a key factor when choosing between these two types of filters.
| Feature | HEPA Filters | ULPA Filters | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Particle Size | 0.3 microns | 0.1 microns | Cost and maintenance are higher |
| Airflow Resistance | Moderate | Higher | Increased energy consumption |
| Typical Use | Air purifiers, HVAC systems | Microelectronics, labs | Larger size and weight |
Choose based on your specific filtration needs and budget.
Standards and Certifications for HEPA and ULPA Filters

Standards and certifications guarantee HEPA and ULPA filters meet strict performance criteria, giving you confidence in their effectiveness. These certifications confirm filters have been tested and verified to trap a specific percentage of particles, depending on their classification. For example, HEPA filters must capture at least 99.97% of 0.3-micron particles, while ULPA filters trap 99.999% of particles down to 0.12 microns. Certifications like those from the U.S. Department of Energy or the European EN standards validate these claims. When selecting a filter, look for labels indicating compliance with recognized standards. Key points include:
- Compliance with industry standards (e.g., HEPA, ULPA)
- Certification from recognized agencies
- Verified particle removal efficiency
- Proper testing procedures
- Clear labeling on the filter product
Choosing the Right Filter for Your Environment

Choosing the right filter depends on evaluating your environment’s specific needs and conditions. First, consider the level of contamination present. If you’re dealing with general dust or allergens, a HEPA filter usually suffices. For environments requiring ultra-clean conditions, like semiconductor manufacturing or pharmaceuticals, ULPA filters are better suited due to their higher efficiency. Think about airflow requirements and filter size. ULPA filters tend to have higher pressure drops, so ensure your system can handle the increased resistance. Also, assess maintenance needs and costs. HEPA filters are generally more affordable and easier to replace. Finally, consider regulatory standards and safety requirements specific to your industry. Making an informed choice guarantees ideal filtration without unnecessary expense or performance issues.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Do HEPA and ULPA Filters Differ in Design and Construction?
You’re curious about how HEPA and ULPA filters differ in design and construction. HEPA filters are built with tightly woven fibers that trap at least 99.97% of particles as small as 0.3 microns, using layered pleats for surface area. ULPA filters are constructed with even finer fibers, capturing 99.999% of particles down to 0.12 microns, often featuring denser media and more layers for maximum filtration efficiency.
Are HEPA or ULPA Filters More Environmentally Friendly?
When comparing the environmental friendliness of HEPA and ULPA filters, you should consider their manufacturing and disposal impacts. HEPA filters generally use less material and energy to produce, making them slightly more eco-friendly. ULPA filters, with their denser construction, may consume more resources and energy during manufacturing and disposal. However, both filters improve indoor air quality, which benefits overall health and reduces pollution indoors.
Can HEPA or ULPA Filters Be Reused or Cleaned Effectively?
You might wonder if HEPA or ULPA filters can be reused or cleaned effectively. Generally, HEPA filters are single-use because cleaning can damage their fibers, reducing efficiency. ULPA filters are also not designed for cleaning and reuse. Instead, replacement is recommended to maintain filtration performance. Always check the manufacturer’s guidelines, as attempting to clean these filters improperly can compromise their ability to trap airborne particles.
What Are the Typical Lifespan and Replacement Intervals?
You’re wondering about the lifespan and when to replace your filters. Typically, HEPA filters last 6 to 12 months, depending on usage and environment, while ULPA filters might last a bit longer, around 1 to 2 years. Regular inspections and airflow measurements help determine when replacement is needed. Keep an eye on performance and replace filters promptly to maintain peak filtration and protect your environment effectively.
How Do Noise Levels Compare Between HEPA and ULPA Filtration Systems?
Imagine a whisper so quiet, it’s almost nonexistent—that’s how ULPA systems often compare to HEPA filters in noise levels. ULPA filters tend to operate more quietly because they use denser media, though this can vary based on design. You’ll generally find ULPA filters produce less noise during operation, making them ideal for environments needing near-silence, like laboratories or cleanrooms. So, ULPA filters usually sound less like a jet engine and more like a gentle breeze.
Conclusion
Choosing between HEPA and ULPA filters is like picking the right net for catching tiny fish—you want one that’s precise enough to do the job. Whether you need a filter for a hospital or a cleanroom, understanding their differences guarantees you make the best choice. Remember, investing in the right filter is like planting seeds for a healthier environment—precise, reliable, and essential for success. Your environment’s purity depends on it.