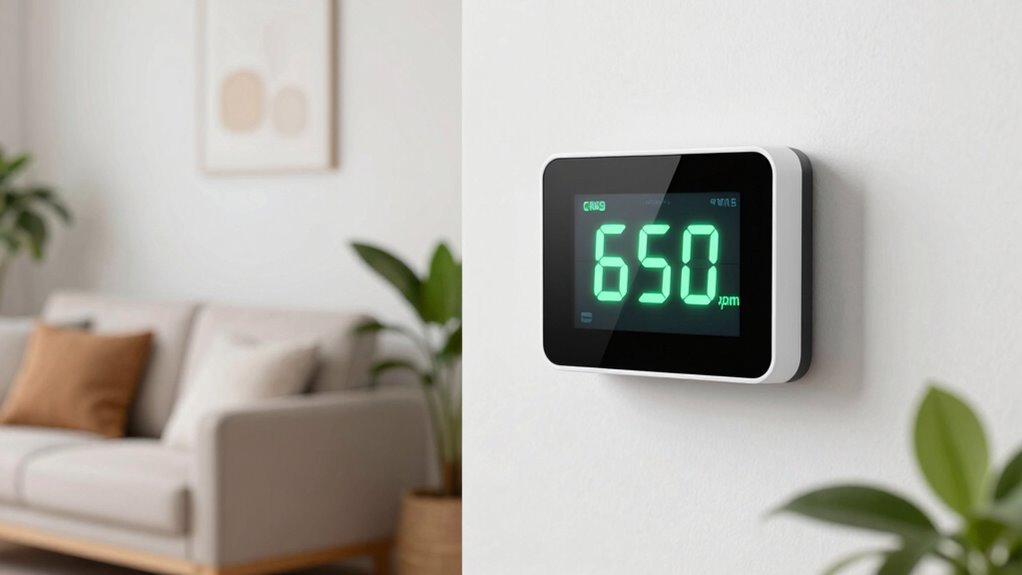
If you see indoor CO2 levels rise, don’t panic—think of it as a signal to check your ventilation. Typical good air quality is around 400-600 ppm, similar to outdoors, while over 800 ppm suggests you might need more fresh air. Levels above 1,000 ppm can cause drowsiness, so increase airflow when needed. Staying calm and understanding what the numbers mean helps you maintain a healthy space—keep reading to learn more.
Key Takeaways
- Recognize that CO2 levels around 400-600 ppm are normal; higher readings indicate the need for better ventilation.
- Understand that levels over 800 ppm suggest insufficient airflow but are not an emergency.
- Use real-time sensor data to assess indoor air quality and identify when to increase ventilation.
- Increase airflow gradually by opening windows or activating fans when CO2 rises above 800 ppm.
- Remember that consistent monitoring helps you manage air quality proactively without unnecessary worry.
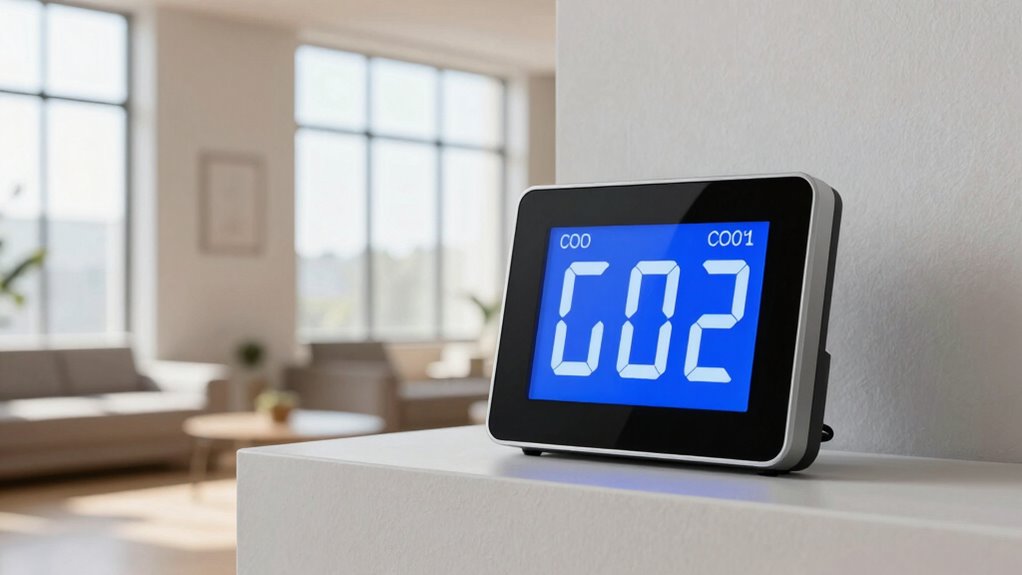

Have you ever wondered what the levels of carbon dioxide (CO2) inside your home or office say about your indoor environment? When you notice the numbers on your air quality sensors, it’s natural to feel concerned, especially if they seem high. But understanding what those readings mean can help you make smarter decisions rather than panicking. The key lies in knowing how to interpret the data and what steps to take.
First, consider the role of ventilation strategies. Proper ventilation is your first line of defense against elevated CO2 levels. If your indoor space is poorly ventilated, CO2 accumulates quickly, signaling that fresh air isn’t circulating enough. Simple fixes like opening windows or using exhaust fans can dramatically improve air exchange. For spaces that lack natural airflow, mechanical ventilation systems—such as HVAC with fresh air intake or energy recovery ventilators—can maintain healthy CO2 levels consistently. These strategies aren’t just about comfort; they directly influence indoor air quality and help prevent the buildup of pollutants, including CO2.
Ensure good ventilation with windows, exhaust fans, or mechanical systems to maintain healthy indoor CO2 levels.
Next, it’s important to rely on your air quality sensors as reliable guides. Modern sensors provide real-time data, giving you instant feedback on your indoor environment. A reading of around 400-600 parts per million (ppm) usually signifies good air quality, similar to outdoor levels. When numbers creep above 800 ppm, it’s a sign that you should improve ventilation. At levels over 1,000 ppm, you might start feeling drowsy or less alert—indicators that your indoor air quality needs attention. But don’t panic; these readings are simply signals that adjustments are needed. Regularly monitoring with air quality sensors helps you identify patterns—such as times of day or activities that cause spikes—so you can plan your ventilation strategies accordingly. Understanding CO2 levels can help you better interpret sensor data and respond effectively.
Understanding the significance of these numbers empowers you to act proactively. You don’t have to overhaul your entire system overnight but instead implement small, manageable changes. For example, increasing airflow during meetings or cooking can prevent CO2 from reaching uncomfortable levels. Combining the use of air quality sensors with effective ventilation strategies creates an environment where you can breathe easier and stay alert. Remember, high CO2 levels are not an emergency—they’re a call to improve your indoor air quality. By paying attention to your sensor readings and adjusting your ventilation habits, you’re taking control of your indoor environment, ensuring it remains safe, comfortable, and healthy.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Are Safe CO2 Levels for Children and Infants?
You should aim for indoor CO2 levels below 800 ppm for children and infants. To guarantee safety, use proper ventilation strategies and place sensors at child’s breathing height for accurate readings. If levels rise, increase ventilation promptly. Keep a close eye on the sensor, and remember that consistent, good airflow helps maintain healthy indoor air quality, reducing risks associated with elevated CO2 for your little ones.
How Does Outdoor Pollution Affect Indoor CO2 Readings?
Outdoor pollution influence can raise your indoor CO2 levels, especially if your home isn’t well-ventilated. When outdoor air quality impact is high due to pollution, it often brings in contaminated air, which increases CO2 readings indoors. You should monitor these levels regularly, open windows when pollution levels drop, and use air purifiers to maintain healthy indoor air quality. Staying aware of outdoor pollution helps you manage indoor CO2 effectively.
Can Plants Significantly Reduce Indoor CO2 Concentrations?
Imagine you’re a modern-day Marie Antoinette, contemplating your garden. Plants can considerably reduce indoor CO2 through plant absorption, but their effectiveness depends on proper air circulation. You should place multiple plants around your space and make sure good airflow to maximize their benefits. While they help, don’t rely solely on plants—combine them with ventilation for the best reduction in CO2 levels.
Are There Differences in CO2 Levels Across Various Building Types?
Yes, CO2 levels vary across building types due to differences in building variations and ventilation impact. You’ll find higher concentrations in enclosed spaces like offices or gyms with limited airflow, while well-ventilated homes or industrial buildings tend to have lower levels. Recognizing these differences helps you understand the importance of proper ventilation. Regularly monitor CO2 levels to guarantee indoor air quality stays healthy, no matter the building type.
How Often Should I Calibrate My CO2 Monitor for Accuracy?
Calibrate your CO2 monitor regularly to guarantee accuracy maintenance. You should do this every 6 to 12 months, or whenever the readings seem inconsistent or suspicious. Frequent calibration keeps your monitor reliable and precise, preventing panic from misleading numbers. By sticking to a calibration schedule, you safeguard your space’s air quality, stay confident in your readings, and maintain peace of mind knowing your CO2 levels are correctly monitored.
Conclusion
So, next time you see those CO2 numbers soaring, don’t panic—just remind yourself it’s nature’s way of telling you to open a window, not buy an air purifier. After all, who needs fresh air when you can just breathe in that cozy, enclosed vibe? Remember, a little excess CO2 is a small price to pay for the luxury of pretending you’re in a sealed bubble—until you realize you’re not.