To treat smelly ear wax, start by using a 3% hydrogen peroxide solution to soften and break it up. Just apply a few drops in your ear twice a day for up to four days. You can also use warm olive or almond oil to help. Use an eyedropper to apply 2-4 drops, then gently massage your ear to enhance absorption. If the odor persists or if you notice pain, fever, or discharge, it's time to consult a professional. Curious about more methods and precautions? You'll find plenty of helpful insights on effective ear care techniques.
Key Takeaways
- Use hydrogen peroxide to soften earwax and reduce odor; apply a few drops twice daily for up to four days.
- Warm olive or almond oil can help soften earwax; apply 2-4 drops and gently massage the ear.
- Consider gentle irrigation with a saline solution to flush out excess wax and odor; seek professional advice if needed.
- Maintain good ear hygiene and avoid cotton swabs to prevent pushing wax deeper and causing impaction.
- Consult a healthcare professional if foul-smelling earwax persists, as it may indicate an infection or other underlying issues.
Understanding Ear Wax and Its Odor

Earwax, often overlooked, plays a crucial role in protecting your ears, but its odor can be a concern. It's produced by ceruminous and sebaceous glands in your ear canal, combining secretions with skin flakes, dust, and debris. This mixture traps harmful particles, preventing them from reaching your eardrum. Interestingly, the type of earwax you have—wet or dry—is determined by your genetics, specifically the ABCC11 gene.
The odor of earwax can arise from several factors. Some people's earwax contains a chemical that wards off insects, which might contribute to the smell. Additionally, dead skin cells and bacteria can lead to unpleasant odors. If you notice a foul smell, it might signal an ear infection or another underlying condition that needs attention. Smelly earwax can indicate underlying issues that may require further investigation.
Hygiene plays a significant role in earwax odor, as poor cleaning can lead to a buildup of sweat and sebum, which combine with bacteria to create an unpleasant scent. Environmental factors, like pollution or hair products, can also influence earwax smell. Understanding these aspects will help you manage any odor concerns effectively.
Benefits of Hydrogen Peroxide

When dealing with smelly earwax, hydrogen peroxide can be a valuable ally in your ear hygiene routine. This simple solution works by releasing oxygen that softens, breaks up, or even dissolves earwax, making it easier for you to clear it out. As it fizzes and bubbles in your ear, it's actively oxidizing the wax, which helps prevent clogs and keeps your ears clear. Additionally, hydrogen peroxide can be effective in removing earwax buildup, helping to maintain ear health.
Using a 3% hydrogen peroxide solution is generally safe when applied in small amounts. However, it's important not to use it if you have an ear infection, a perforated eardrum, or tympanostomy tubes. Start with a minimal dose to test for any irritation or discomfort. To apply, lie on your side with the affected ear up, then administer the appropriate number of drops and stay still for about 5-10 minutes to let it penetrate.
You can use hydrogen peroxide twice daily for up to four days. Plus, it has a weak antibacterial effect, which can help prevent infections. If hydrogen peroxide doesn't work, consult a doctor for alternative treatments like irrigation or microsuction.
Softening Wax With Oils
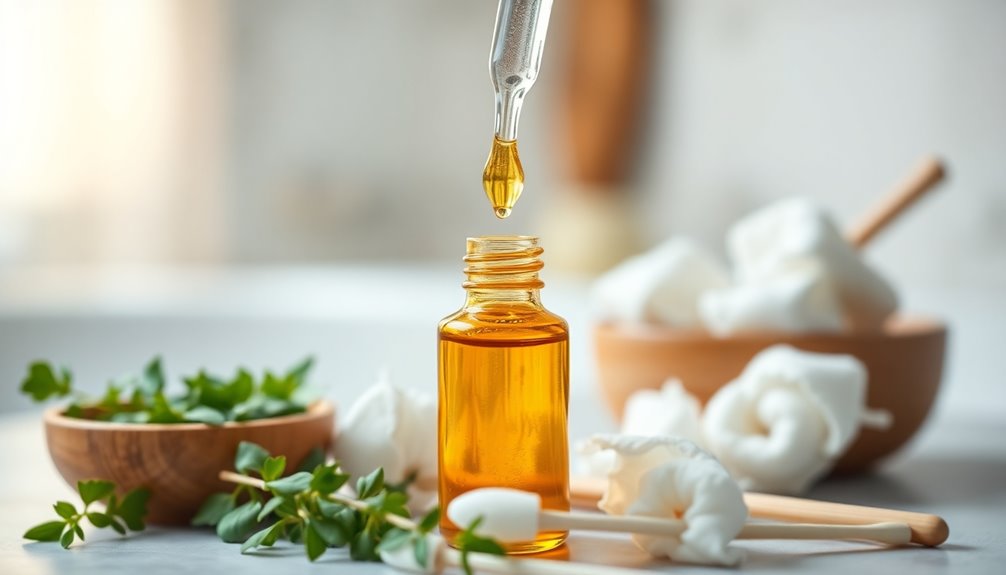

Softening earwax with oils can be an effective and gentle method to clear blockages and reduce odor. Olive oil is a popular and gentle choice, but you can also use almond oil, mineral oil, baby oil, or arachis oil. For a less common option, try rectified camphor oil.
To apply the oil, warm it between your hands to reach a comfortable temperature. Using an eyedropper, place 2-4 drops of warm oil into the affected ear while lying on your side with that ear facing up. Gently massage the front and back of your ear to help the oil penetrate. Stay in this position for at least ten minutes to allow the oil to work effectively. It is important to note that chemical and oil-based methods may take longer to show effectiveness, which is something to consider during treatment.
Repeat this process twice a day until the wax is cleared, and if needed, continue for several days. For preventive care, consider using oil once a week. Keep in mind that if you're using olive oil, it may take a bit longer to see results. Always check for allergies, avoid applying hot oil, and be mindful of potential side effects like itching or irritation, especially if your eardrum is ruptured.
Effective Irrigation Techniques

Once you've softened earwax using oils, you may need to consider irrigation techniques to clear any remaining buildup effectively. Start by preparing a gentle irrigation solution, ensuring it's at a comfortable temperature between 98.6°F and 104.9°F (37.0°C and 40.5°C). Position yourself with the affected ear facing upward, and gently pull the upper ear back and slightly up to straighten the ear canal.
Using a syringe, squirt the solution near the ear opening, avoiding direct contact with the eardrum to prevent pain or injury. Keep the volume limited to 500 ml to avoid pressure buildup. If you feel any pain or dizziness during the process, stop immediately. It's crucial to maintain cleanliness, so use disposable equipment and clean the outer ear with normal saline beforehand. After irrigation, ensure no water remains in the ear to prevent bacterial growth. If you notice any complications or have concerns, consult a healthcare provider.
Remember, don't perform this procedure if you suspect an ear infection, cold, or other contraindications. Trained personnel are essential for ensuring safety during ear irrigation—safety first—these precautions can help you safely manage earwax buildup!
Home Remedies for Ear Wax

For those looking to manage ear wax at home, several effective remedies can help soften and remove buildup. Hydrogen peroxide mixed with equal parts water can be applied using a dropper to gently soften wax. If you prefer natural oils, baby oil, coconut oil, and almond oil are excellent choices for lubricating and breaking down ear wax.
You can also try saline solutions; mixing one teaspoon of salt in half a cup of warm water can help. Use a rubber bulb syringe to gently irrigate your ear with warm water, aiding in wax removal. Glycerin and apple cider vinegar (diluted) are other options to consider. Additionally, warm water is a gentle irrigation method that helps flush out debris from the ear canal.
Household ingredients like baking soda and garlic can be effective as well. Baking soda dissolved in water can help break down hardened wax, while garlic offers antibacterial properties that reduce infection risks.
For a more targeted approach, over-the-counter ear drops containing carbamide peroxide can be beneficial. Remember to dry your ear canal with a cotton swab or towel after any irrigation. Avoid using olive oil and ear candling, as they may cause irritation or harm.
Important Precautions to Consider

When it comes to managing ear wax, taking important precautions is essential to avoid potential harm. You might be tempted to use sharp objects like hairpins or tweezers, but these can scratch or cut the delicate skin of your ear canal. Worse, they could even puncture your eardrum, leading to pain and hearing loss. DIY methods often push wax deeper, increasing the risk of cerumen impaction, which may require medical treatment.
Inserting foreign objects can disturb the natural bacteria in your ear, raising your risk of infection. Removing too much wax disrupts your ear's defense against bacteria, while washing can upset the pH balance, making your ear more vulnerable. Excessive ear wax creates a perfect environment for infections.
Be cautious with common practices like using cotton swabs or even your fingers, as these can push wax deeper and cause blockages. Stay away from ear candles and sharp tools, as they can lead to burns or injuries. Always consult a healthcare professional before attempting any ear wax removal, especially if you experience symptoms like pain or decreased hearing. Your ears deserve safe and effective care!
When to Seek Professional Help

If you notice persistent symptoms related to your ears, it's crucial to seek professional help. An earache that doesn't go away, fever, or drainage from the ear can indicate a more serious issue. Additionally, if you detect a foul odor coming from your ear or experience persistent itchiness, these symptoms warrant a visit to a healthcare provider.
Specific conditions also signal the need for medical attention. If you're facing hearing loss, dizziness, or tinnitus, don't ignore these signs. A feeling of fullness in the ear or a cough connected to earwax blockage should prompt a consultation as well. Excessive earwax can lead to these symptoms, making it important to address any earwax issues promptly. Background checks can identify potential health risks that might affect your overall well-being.
Watch for signs of potential complications, like watery, smelly discharge, redness, or swelling around the ear. Pain, especially if accompanied by fluid or blood leaking after a head injury, is another red flag. Lastly, if your symptoms persist or worsen over time, or if you have a history of ear infections or ear surgery, it's time to consult a professional. Addressing these issues early on can help prevent more serious conditions and ensure your ear health remains intact.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can Diet Affect the Smell of Ear Wax?
Yes, your diet can definitely affect the smell of your ear wax. Foods high in sugar, processed items, and dairy can lead to changes in ear wax consistency and odor. If you consume a lot of spicy foods or caffeine, you might notice a stronger smell as well. By reducing these foods and focusing on a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and omega-3s, you can help maintain healthier ear wax and minimize unpleasant odors.
Is It Safe to Use Vinegar in the Ear?
Using vinegar in your ear can be risky if not done correctly. You should always dilute it with equal parts water to avoid irritation or burns. If you have any signs of infection, like drainage or fever, skip the vinegar and consult a doctor instead. For mild outer ear issues, vinegar might help, but it's crucial to monitor your symptoms and stop using it if discomfort arises. Always prioritize your ear health!
How Often Should I Clean My Ears?
You should clean your ears based on your ear wax production and symptoms. For most people, once a year is enough, but if you notice muted hearing or discomfort, consider cleaning every six months. If you produce excessive wax, quarterly cleaning might be necessary. Always listen to your body—if you have symptoms like pain or fullness, you might need to clean sooner. Just remember, avoid cotton swabs as they can push wax deeper.
Can Stress Influence Ear Wax Production?
Yes, stress can definitely influence ear wax production. When you're stressed, your body releases cortisol, which can lead to an increase in cerumen production. You might notice more oily secretions around your ear canal, indicating heightened stress levels. This buildup can cause blockages, affecting your hearing and potentially leading to discomfort. Managing your stress levels is essential for overall ear health, so try relaxation techniques to help reduce its impact on your body.
Are There Any Allergies Related to Ear Wax Treatments?
Yes, there can be allergies related to ear wax treatments. You might experience hives, difficulty breathing, or swelling in your face or throat after using certain ear drops. Mild itching or a feeling of fullness in your ear can also occur. Always follow your healthcare provider's guidance when using ear drops, and be cautious if you have a history of allergic reactions. If you notice any severe symptoms, seek medical attention immediately.
Conclusion
In conclusion, tackling smelly ear wax doesn't have to be complicated. By understanding the causes and using simple remedies like hydrogen peroxide or natural oils, you can effectively manage the odor. Just remember to follow safe irrigation techniques and take necessary precautions. If the problem persists or worsens, don't hesitate to seek professional help. Your ears deserve care, so keep them clean and odor-free for better comfort and health!