Food allergies can cause a variety of skin reactions, such as hives, eczema flare-ups, swelling (angioedema), and contact dermatitis. Hives often appear quickly as itchy, raised welts, while eczema may worsen after eating certain foods like dairy or nuts. Severe reactions like angioedema can block airways and need urgent care. Recognizing these signs helps you respond appropriately. Continual awareness can help you better manage symptoms and prevent serious complications; here’s more to understand.
Key Takeaways
- Food allergies can cause immediate skin reactions like hives, swelling, redness, and eczema flare-ups.
- Hives are a common sign of allergic responses, appearing suddenly within minutes to hours after eating allergenic foods.
- Contact dermatitis results from direct food contact, leading to redness, itching, swelling, or blisters on the skin.
- Severe reactions like angioedema may cause swelling of deeper skin layers, affecting the face, lips, or throat, requiring urgent care.
- Managing skin manifestations involves identifying and avoiding triggers, using antihistamines or corticosteroids, and seeking medical attention when needed.
Common Skin Reactions Linked to Food Allergies

Food allergies often cause a variety of skin reactions that can be both immediate and noticeable. You might notice swelling, redness, or irritation after eating certain foods. Hives, or raised, itchy welts, are common and can appear suddenly, often spreading across your skin. Eczema flare-ups may worsen, leading to dry, cracked, and inflamed skin. Some people experience itching or burning sensations, especially around the mouth or face. Swelling, known as angioedema, can occur in deeper skin layers, causing puffiness, particularly around the eyes, lips, or throat. These reactions are your body’s way of responding to an allergen, signaling that your immune system perceives the food as harmful. Recognizing these skin signs early helps you seek proper treatment and avoid more severe allergic responses. Additionally, innovative materials in products like jewelry and footwear are increasingly being used to reduce allergic reactions and skin sensitivities.
How Hives Indicate Food Allergic Responses
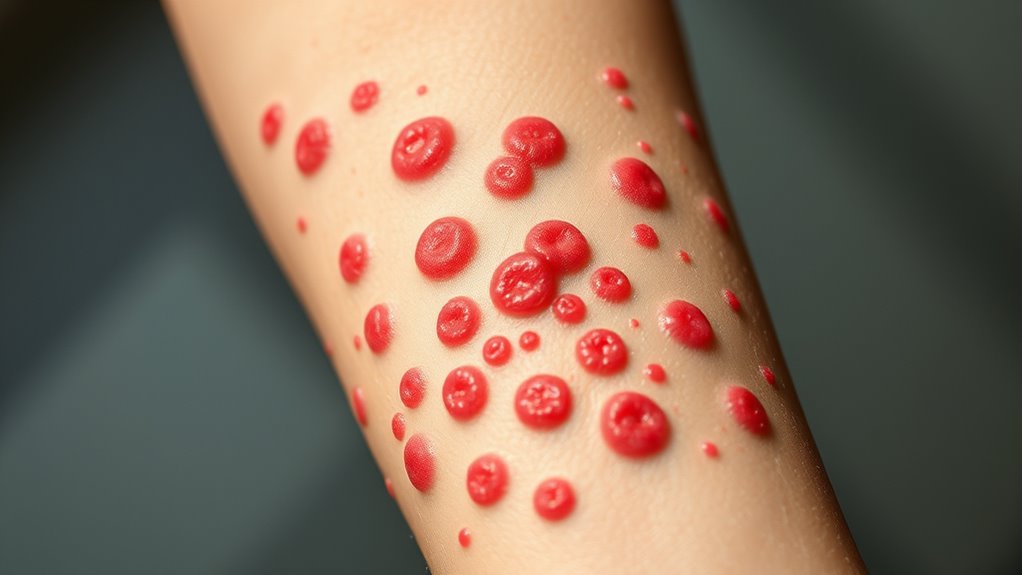
Hives, also known as urticaria, are a common and immediate sign of a food allergy response. When you consume a food you’re allergic to, your immune system releases histamine, causing your skin to react. This reaction results in raised, red, and itchy welts that can appear suddenly. Hives often develop quickly, sometimes within minutes to hours after eating. They can vary in size and shape, often merging together to form larger areas of swelling. You might notice hives on your face, arms, or other parts of your body. The rapid onset and distinctive appearance make hives a key indicator that your body is reacting allergically to a particular food. Recognizing these signs allows you to seek prompt treatment and avoid further exposure. Understanding immune responses can help you better comprehend why these skin manifestations occur.
Eczema and Its Connection to Food Sensitivities

You might notice your eczema worsening after eating certain foods, which could be triggers. Identifying these food sensitivities is key to controlling flare-ups and improving your skin. Managing your diet and recognizing patterns can make a real difference in your eczema symptoms. Understanding allergic reactions and their impact on skin health can further aid in managing sensitivities effectively.
Eczema Triggers From Foods
Eczema symptoms can often flare up when the body reacts to certain foods, revealing a direct link between diet and skin health. Common food triggers include dairy, eggs, soy, wheat, and nuts. When you consume these foods, your immune system may overreact, causing inflammation that worsens eczema symptoms. You might notice increased itching, redness, or dry patches after eating specific items. Keep in mind, triggers vary from person to person, and sometimes even small amounts can cause a reaction. Recognizing these triggers is essential, but it’s equally important to avoid unnecessary restrictions without proper guidance. By paying attention to how your skin responds to different foods, you can better manage flare-ups and reduce the severity of your eczema episodes. Understanding food sensitivities can help you identify subtle reactions and avoid potential aggravators.
Identifying Food Sensitivities
Recognizing which foods trigger eczema flare-ups can be challenging because reactions vary widely from person to person. You might notice a flare after eating dairy, nuts, or gluten, but not everyone reacts the same way. To identify sensitivities, keep a detailed food diary, noting what you eat and any skin changes. This helps you spot patterns over time. Consider eliminating suspected foods one at a time for a few weeks to see if your symptoms improve. Consulting with a healthcare professional or allergist can provide guidance, and they may recommend tests like elimination diets or blood work. Remember, patience is key—finding your triggers takes time and careful observation. By staying vigilant, you can better understand your individual sensitivities and reduce eczema flare-ups.
Managing Skin Flare-ups
Managing skin flare-ups involves identifying and avoiding the foods that trigger your eczema symptoms. When you notice flare-ups, track your diet to pinpoint potential culprits. Eliminate common triggers like dairy, eggs, or nuts, and observe if your skin improves. Incorporate gentle skincare routines—use moisturizers and avoid harsh soaps—that help soothe irritated skin. Applying topical corticosteroids or antihistamines can provide quick relief, but always follow your doctor’s advice. Remember, managing flare-ups isn’t just about avoiding foods; it’s about maintaining overall skin health. Stay consistent with your skincare and dietary adjustments, and communicate any changes or persistent symptoms to your healthcare provider. Consistent use of appropriate skincare products can significantly reduce inflammation and support skin barrier repair. With patience and careful management, you can reduce the frequency and severity of eczema flare-ups effectively.
Angioedema: Swelling Beneath the Skin Due to Allergies
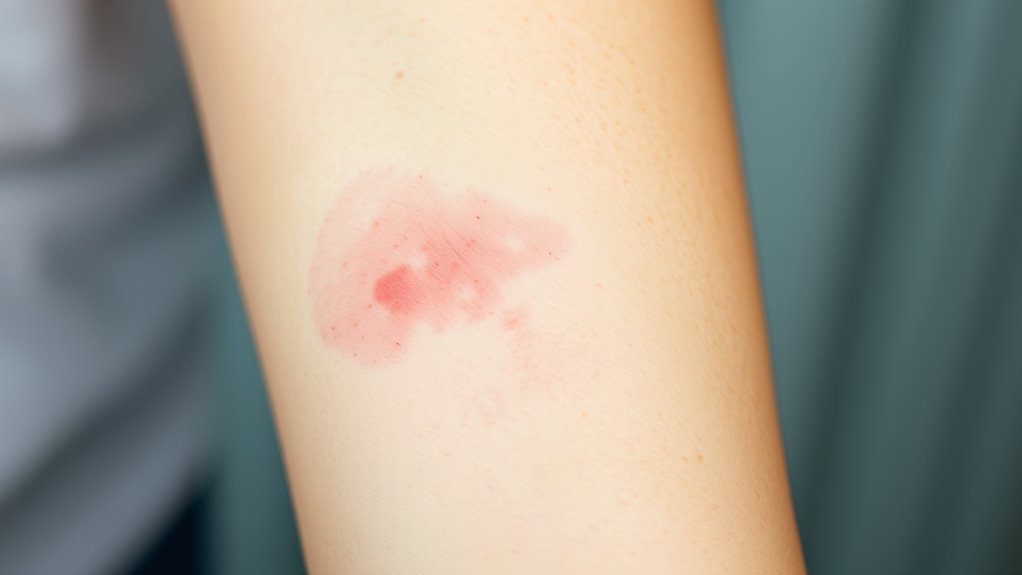
Angioedema causes sudden swelling beneath your skin, often linked to allergic reactions like food allergies. You might notice signs such as swelling around your eyes, lips, or throat, which can be uncomfortable or even dangerous. Understanding its causes, symptoms, and treatment options helps you respond effectively and prevent serious complications. In some cases, angioedema may be associated with immune response mechanisms, which play a role in allergic reactions.
Causes of Angioedema
Angioedema occurs when blood vessels beneath the skin become more permeable, allowing fluid to escape into surrounding tissues and cause swelling. This process is often triggered by immune responses or other factors that activate your body’s inflammatory pathways. Common causes include allergic reactions to foods like nuts, shellfish, or eggs, and medications such as ACE inhibitors. Sometimes, genetic factors or physical triggers like pressure or cold can also induce angioedema. Understanding these causes helps you identify potential triggers and seek prompt treatment. Here’s a quick overview:
| Cause Type | Example |
|---|---|
| Allergic reactions | Nuts, shellfish, pollen |
| Medication-induced | ACE inhibitors, NSAIDs |
| Physical triggers | Cold, pressure, sunlight |
| Genetic predisposition | Hereditary angioedema |
| Idiopathic (unknown) | No identifiable trigger |
Symptoms and Signs
When angioedema occurs, the swelling beneath your skin becomes noticeable through sudden, often painless, firmness or puffiness. You might see this swelling around your eyes, lips, or face, sometimes spreading quickly. The affected area feels firm and may look shiny or swollen. Unlike skin rashes, angioedema doesn’t usually itch, but the swelling can be uncomfortable or alarming. It may develop rapidly after exposure to an allergen, such as certain foods. In some cases, the swelling affects deeper layers of skin, creating a visible bulge that lasts from a few hours to a couple of days. You might also notice tenderness or a feeling of tightness in the swollen areas. Recognizing these signs early helps in managing the reaction effectively. Understanding the physical effects of allergic reactions can support prompt identification and treatment.
Treatment Options
If you experience swelling beneath your skin due to allergies, prompt treatment can help reduce symptoms and prevent complications. The first step is to identify and avoid the allergen responsible. Over-the-counter antihistamines can help relieve swelling and itching by blocking allergic responses. For more severe reactions, your doctor might prescribe corticosteroids to reduce inflammation. In cases of acute angioedema, especially if it affects your airway or causes difficulty breathing, you should seek emergency care immediately. In some instances, an epinephrine injection may be necessary to quickly counteract severe swelling. Long-term management may involve allergy testing to identify triggers and develop an action plan. Additionally, advancements in AI in Education are exploring personalized learning approaches that could someday assist in allergy education and management. Always consult your healthcare provider for personalized advice and to determine the most effective treatment approach.
Recognizing Contact Dermatitis From Food Contact

Contact dermatitis from food contact occurs when your skin reacts to direct exposure to certain foods or food residues. You might notice redness, itching, swelling, or even blisters where the food touched your skin. This reaction often develops quickly after contact, especially if you have a sensitivity or allergy to that food. Common sources include handling food with allergenic ingredients, touching food packaging, or coming into contact with food residues on dishes or utensils. You may also see dry or cracked skin in the affected area. Recognizing these signs helps you identify potential food triggers and avoid further contact. Keep an eye out for localized skin changes, especially if they appear after handling specific foods or food containers. Using protective gloves or barrier creams can help reduce the risk of allergenic contact during food handling.
Severe Skin Reactions: Anaphylaxis and Its Manifestations
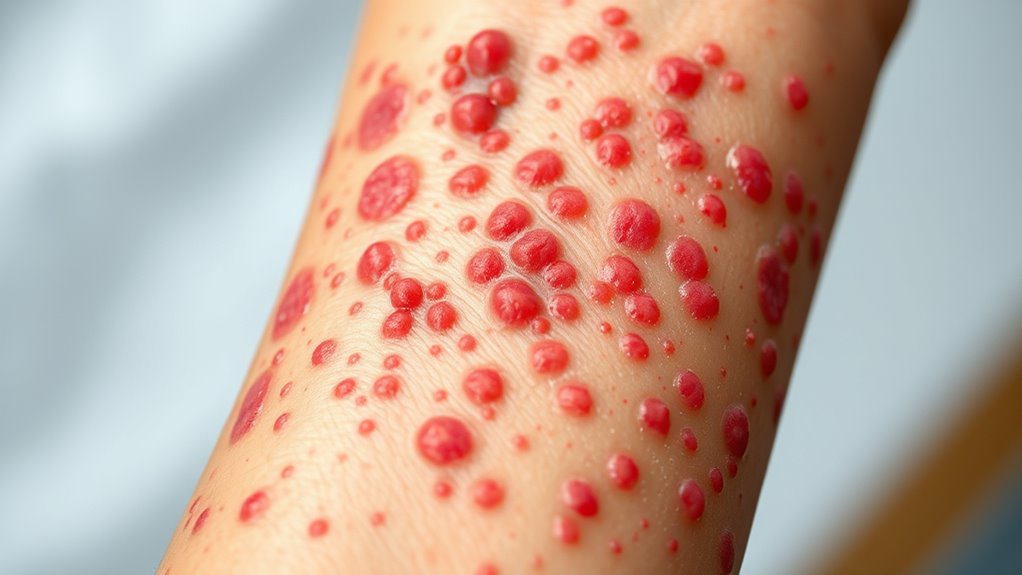
Severe skin reactions such as anaphylaxis can occur rapidly and require immediate attention. If you notice hives, swelling, or redness spreading quickly after eating, seek emergency help immediately. Anaphylaxis can cause your airway to swell, making breathing difficult, or lead to a sudden drop in blood pressure, resulting in dizziness or fainting. Skin manifestations often appear as widespread hives or flushing, but these are signs of a more serious reaction. It’s essential to recognize these symptoms early and act fast. Administering an epinephrine auto-injector can be lifesaving, but you must still get medical care right away. Never ignore severe skin changes after consuming potential allergens—quick response can prevent life-threatening complications. Being aware of allergy symptoms can help you respond promptly and effectively.
Differentiating Food Allergy Skin Symptoms From Other Conditions
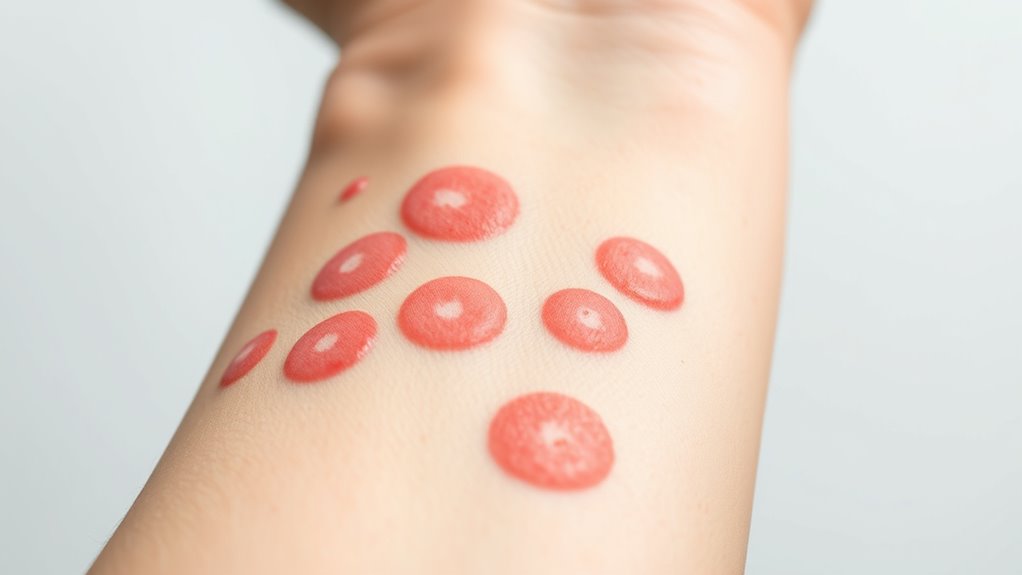
Differentiating food allergy skin symptoms from other conditions requires careful observation, as many skin issues can look similar but have different causes. To tell them apart, consider these factors:
- Onset and timing: Food allergy reactions often occur quickly after eating, usually within minutes to a few hours. Other conditions, like eczema or contact dermatitis, develop more gradually.
- Appearance and distribution: Food allergy reactions typically cause hives—raised, itchy welts that can appear suddenly and change location. Chronic skin conditions tend to have a more consistent pattern.
- Associated symptoms: Food allergies may come with additional signs like swelling, stomach upset, or breathing difficulties, which are less common in other skin disorders.
Careful observation helps identify whether a skin reaction is food-related or due to another cause.
The Role of Skin Testing in Diagnosing Food Allergies
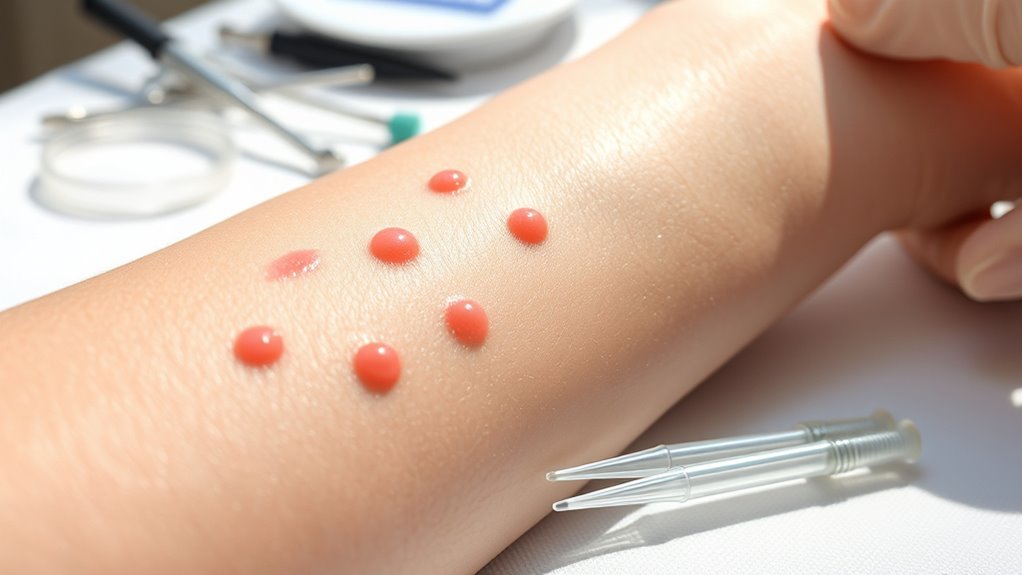
Skin testing plays a crucial role in diagnosing food allergies by providing direct evidence of allergic sensitivities. When you undergo skin testing, small amounts of suspected allergens are introduced into your skin, usually via a prick or scratch. If you’re allergic, you’ll develop a localized skin reaction, such as redness or swelling, within minutes. This immediate response helps identify specific foods that trigger your symptoms. Skin testing is quick, minimally invasive, and highly useful in guiding allergy management. However, it’s important to remember that positive results do not always mean a true allergy—sometimes, false positives occur. Consequently, skin tests are best used alongside your medical history and, if needed, confirmatory tests like oral food challenges.
Strategies for Managing and Preventing Skin Reactions

To effectively manage and prevent skin reactions caused by food allergies, it’s essential to adopt proactive strategies that minimize exposure and reduce sensitivity. First, always read food labels carefully, looking for hidden ingredients that could trigger a reaction. Second, communicate your allergies clearly when dining out, informing staff about your sensitivities. Third, keep an emergency kit handy with antihistamines and topical treatments to address reactions promptly. Additionally, identify and avoid cross-reactive foods that may worsen your skin symptoms. Regularly consult with your healthcare provider to adjust your allergy management plan. Implementing these steps helps reduce the risk of skin reactions, keeps symptoms under control, and improves your overall quality of life.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can Food Allergies Cause Skin Symptoms Without Other Systemic Reactions?
You might wonder if skin symptoms can appear without other systemic reactions. Yes, it’s possible. You could experience skin issues like hives, itching, or swelling solely from a food allergy, even if you don’t notice any other symptoms like stomach pain or breathing problems. These skin reactions happen because your immune system reacts locally to the allergen, causing noticeable skin changes without affecting other parts of your body.
Are There Specific Foods More Likely to Cause Skin Reactions?
Imagine a garden where certain plants are more likely to cause weeds to flourish. Similarly, specific foods like nuts, shellfish, eggs, and dairy are more prone to trigger skin reactions. You might notice redness, hives, or itching after consuming these. Just as some plants are invasive, these foods often provoke immune responses, making them common culprits. Stay alert to your body’s signals and consult your healthcare provider for personalized advice.
How Long Do Skin Reactions Typically Last After Eating Allergenic Foods?
When you experience skin reactions after eating, they usually last from a few hours up to a couple of days. The duration depends on factors like the severity of the reaction and your body’s response. You might notice symptoms resolving quickly or lingering longer if the reaction is intense. If symptoms persist beyond a couple of days or worsen, it’s best to consult a healthcare professional for proper evaluation and management.
Can Cooking or Processing Foods Reduce Their Allergenic Potential on Skin Reactions?
Cooking or processing foods can sometimes reduce their allergenic potential, but it’s not a guarantee. You might find that heat denatures certain proteins responsible for reactions, making them less likely to cause skin issues. However, some allergens remain stable even after cooking. So, if you have sensitivities, it’s safest to avoid processed versions of problematic foods or consult your doctor before trying new preparations.
Are Children More Prone to Skin Allergies From Foods Than Adults?
You might wonder if children are more prone to skin allergies from foods than adults. Generally, kids do have a higher risk because their immune systems are still developing, making them more sensitive to certain allergens. Their skin barrier is also more fragile, which can lead to more noticeable reactions. However, individual factors vary, and some adults can also develop or experience worsening food-related skin allergies over time.
Conclusion
Understanding how food allergies affect your skin is vital—you could be one bite away from a reaction that feels like a wildfire spreading across your body. By recognizing symptoms like hives, eczema, or swelling, and seeking proper testing, you take control of your health. Don’t let a hidden allergy turn your life into a battleground. Stay vigilant, manage your triggers, and keep your skin safe—because your well-being is worth more than any fleeting discomfort.