If your earwax smells foul, it's time to pay attention. A bad odor can indicate an ear infection caused by anaerobic bacteria or a buildup of excessive earwax. You might also notice symptoms like pain, itching, or hearing difficulties. Ignoring these signs can lead to serious complications, including hearing loss or debilitating infections. Keeping your ears clean and dry can help, but don't hesitate to seek professional help if you're experiencing ongoing issues. Understanding these warning signals is crucial, and there's more to uncover about your ear health that you won't want to miss.
Key Takeaways
- A foul odor from earwax may indicate an ear infection caused by anaerobic bacteria or other health issues needing attention.
- Symptoms like excessive earwax, earaches, or hearing difficulties often accompany smelly earwax and signal potential infections.
- Seek immediate medical help if experiencing severe pain, high fever, or fluid discharge from the ear, as these can indicate serious conditions.
- Regular ear hygiene and avoiding cotton swabs can prevent earwax buildup and associated odors, promoting overall ear health.
- Home remedies should be approached cautiously; professional evaluation is essential for persistent issues or unusual symptoms.
Understanding Earwax Types
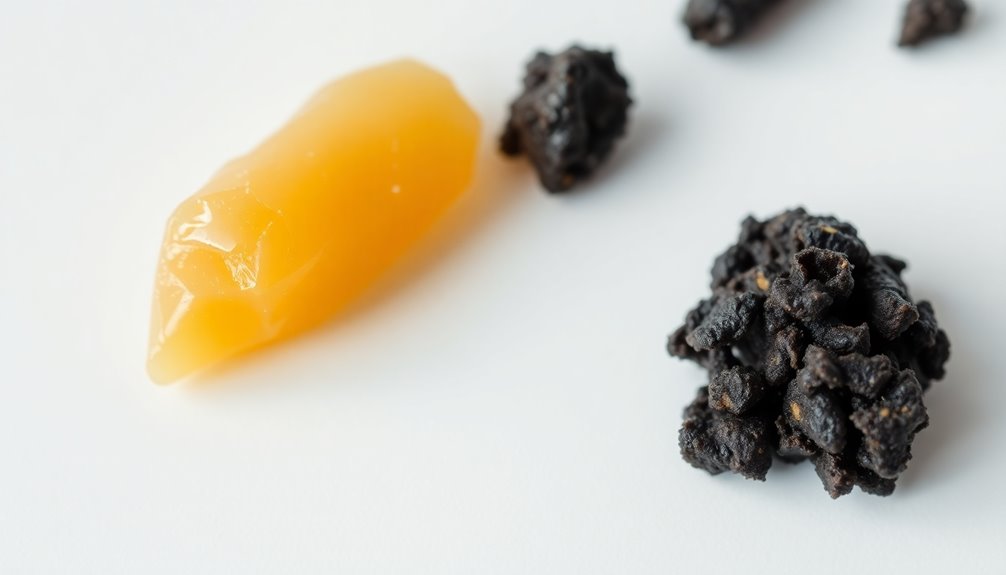

When it comes to earwax, understanding the different types can help you recognize what's normal for you. Your earwax can be categorized as either wet or dry, and this distinction is largely determined by your genetics, specifically the ABCC11 gene.
If you have the wet type, you'll notice it's sticky and viscous, often ranging from dark yellow to brown. This type is common among Caucasians and Africans and has a high lipid content, which can contribute to a stronger body odor. Variations in earwax types can significantly impact personal hygiene and health.
On the other hand, if you have dry earwax, it'll likely appear flaky and brittle, with a gray or tan color. This type is more prevalent in East Asians, Native Americans, and Pacific Islanders, and has a lower lipid content, resulting in less body odor.
Both types serve important functions, like protecting your ear canal from dust and bacteria while maintaining skin moisture.
Pay attention to the color and texture of your earwax, as changes can indicate potential health issues or earwax impactions, helping you stay informed about your ear health.
Identifying Causes of Odor
Identifying the causes of odor in earwax is crucial for maintaining your ear health. A foul smell often signals an ear infection, which is the most common culprit. This type of infection can damage the middle ear and emit a bad odor due to anaerobic bacteria. You might experience symptoms like earache or difficulty hearing, so it's important to seek medical attention.
Another potential cause is a cholesteatoma, a growth in the middle ear that can destroy surrounding bones and lead to an unpleasant smell.
Foreign objects, particularly organic ones, lodged in the ear can also produce smelly earwax, especially in children who sometimes insert small items.
Swimmer's ear, a bacterial infection resulting from trapped water, can cause odor and discomfort. Excessive earwax may trap debris and bacteria, leading to a foul smell; this can come with earaches and hearing difficulties. Regular cleaning can help prevent the buildup of earwax, which contributes to these issues.
Finally, while rare, serious conditions like ear cancer or certain genetic disorders could also be responsible for smelly earwax. If you notice persistent odor alongside other unusual symptoms, consult a doctor to rule out any serious health issues.
Recognizing Associated Symptoms

Recognizing associated symptoms is essential for addressing earwax odor effectively. If you notice a foul smell, pay attention to other symptoms that might accompany it. For instance, excessive earwax can lead to earaches, difficulty hearing, or a sensation of fullness in your ear.
You might also experience itchiness or drainage, which can indicate a buildup requiring attention. It's important to note that smelly earwax can also accumulate bacteria and debris, leading to unpleasant odors.
On the other hand, if there's pain and you find yourself tugging at your ear, especially in children, it could signal an ear infection. Look out for trouble sleeping, increased crying, or even fever. These signs shouldn't be ignored.
If you suspect a foreign object is lodged in your ear, watch for pain, hearing loss, or unusual discharge with an unpleasant odor. Itching and redness inside your ear can also be indicators of an infection.
Lastly, symptoms of swimmer's ear or other infections include persistent itching, mild discomfort, pus, and trouble hearing. If you experience any of these symptoms, it's essential to consult a healthcare professional to address the issue promptly and effectively.
Taking action early can prevent further complications.
Health Implications to Consider
Considering the health implications of earwax odor is crucial for your well-being. A foul smell often indicates a severe infection, likely caused by anaerobic bacteria. This can lead to middle ear damage, resulting in balance issues and phantom noises.
If you experience severe pain, high fever, vomiting, or hearing loss, don't ignore these signs. Infections can escalate into serious conditions like mastoiditis, which may require antibiotics or surgery.
Excessive earwax buildup can also cause impaction, leading to hearing loss, ear pain, and even tinnitus. If your ears feel full or you're experiencing dizziness, it's essential to seek medical attention.
Untreated impaction increases the risk of serious infections, and complications like meningitis or even brain abscesses can arise.
Additionally, smelly earwax might signal underlying medical conditions or foreign objects trapped in your ear. Some genetic links have been noted, while specific conditions like maple syrup urine disease could be detected through earwax analysis. Notably, wet earwax is thought to offer protection against insects, suggesting that earwax characteristics may also reflect evolutionary adaptations.
It's vital to pay attention to these warning signs, as they might reveal more about your overall health. Don't overlook early symptoms; addressing them could prevent serious complications.
Prevention and Maintenance Tips

Maintaining proper ear hygiene and taking preventive measures can significantly reduce the risk of earwax buildup and infections.
First off, avoid using cotton swabs, bobby pins, or any sharp objects to clean your ears. Instead, use a soft, damp washcloth on your finger to gently clean the outer ear. Excessive earwax production can block the ear and create odor, so it's important to manage earwax levels.
After swimming or bathing, keep your ear canal dry by tilting your head to help excess water drain out and using a small, soft towel to soak up any remaining moisture.
To prevent wax buildup, consider using earwax softeners like mineral oil or olive oil. Apply a few drops into your ears once or twice daily for 5-10 minutes. You can also flush your ear with warm water to help remove softened wax.
Avoid wearing earplugs or hearing aids that can push earwax deeper into your ear canal.
Regular cleaning is essential—wash your outer ear with mild soap and warm water. Inspect your ears regularly for excessive wax or signs of infection.
Medical Interventions Available

If you're dealing with an unpleasant earwax odor, seeking medical interventions can be crucial for your ear health. Start by scheduling an appointment with a healthcare provider. They'll evaluate your symptoms to determine if the odor is from earwax or another condition.
Using an otoscope, they can examine your ear canal and eardrum, ruling out infections or middle ear damage. A thorough medical history will help identify any underlying causes. Earwax produced by glands in the ear canal traps dust and particles, contributing to the odor you may be experiencing.
Under medical guidance, your provider might recommend ear drops, like mineral oil or glycerin, to soften the wax. You may also use a 50/50 mix of hydrogen peroxide and warm water to help dissolve it.
However, avoid using ear candles or other folk remedies without consulting your provider first.
For safe earwax removal, it's best to let a healthcare professional handle it. They can use gentle flushing or special tools to clear blockages effectively.
If the odor is linked to an infection, expect possible prescriptions for antibiotics or antifungal medications. Regular follow-ups are essential to ensure your ears stay healthy and any underlying issues are adequately addressed.
When to Seek Help
When you notice persistent ear pain or a strong odor coming from your earwax, it's important to seek help promptly. Ignoring these symptoms can lead to more serious health issues.
If you experience ear pain that doesn't go away, itchiness, or ringing in your ears, don't hesitate to consult a healthcare professional. Hearing loss or dizziness can also indicate underlying problems that need attention.
Pay close attention to any discharge or fluid leaking from your ear. A foul odor accompanying these symptoms, especially if there's redness or swelling, is a clear sign you should seek medical advice. Excessive earwax can lead to symptoms such as pain and hearing loss, which underscores the importance of addressing these issues promptly.
Blood in the discharge or a sudden change in your hearing can signal an immediate need for evaluation.
If you have a fever along with ear symptoms or have recently suffered a head injury with fluid or blood leaking from your ear, seek help right away.
Conditions like middle or outer ear infections, damage to the eardrum, or even the rare possibility of ear cancer need prompt diagnosis and treatment.
Don't wait—your ear health is crucial, and timely intervention can make all the difference.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can Diet Affect the Smell of My Earwax?
Yes, your diet can definitely affect the smell of your earwax.
Consuming dairy, gluten, and high-sugar foods can lead to increased earwax production and odor. Spicy foods and caffeine can also contribute to changes in consistency, making earwax stickier and more prone to blockages.
Staying hydrated and maintaining a balanced diet rich in fruits and omega-3 fatty acids can help keep your earwax healthy and reduce unpleasant smells.
Is It Normal for Earwax Color to Change?
Yes, it's normal for your earwax color to change. Fresh earwax usually appears off-white to yellow, while older earwax can turn yellow to brown as it accumulates debris.
Factors like genetics, diet, and environmental exposure also influence earwax color.
If you notice unusual colors, such as green or blood-tinged, it might indicate an underlying health issue, so it's best to consult a healthcare professional if you're concerned.
How Often Should I Clean My Ears?
You should clean your ears based on your individual needs.
For many, once a year is enough, while others might need to clean them every six months. If you're prone to wax buildup, consider cleaning every three months.
Pay attention to symptoms like muffled hearing or discomfort; they might indicate it's time for a cleaning.
Regular check-ups with a professional can help you determine the best schedule for your ear health.
Does Earwax Smell Different in Children?
Yes, earwax does smell different in children compared to adults.
Typically, children's earwax has a slightly sweet or musty scent, indicating healthy ear function.
As they grow, the texture and color of their earwax change, which can also affect the smell.
If you notice a strong or sour odor, it could signal a potential issue, so it's important to be attentive to any unusual changes and consult a doctor if needed.
Can Stress Influence Earwax Odor?
Yes, stress can influence earwax odor.
When you're stressed, your body releases hormones that can increase earwax production. This heightened production often leads to a stickier, more odorous type of earwax due to the sweat and proteins involved.
Bacteria in the ear metabolize these substances, resulting in foul-smelling compounds.
Conclusion
In conclusion, if you notice a strong odor coming from your earwax, it's essential to pay attention. It might signal an underlying issue that needs addressing. By understanding the types of earwax and recognizing associated symptoms, you can take proactive steps. Don't hesitate to seek help if you're unsure or if the smell persists. Keeping your ears clean and healthy is key, so follow the prevention tips and consult a professional when necessary. Your health matters!