Yes, earwax does have a smell, which can vary based on its type and your health. Generally, healthy earwax has a slightly sweet or musty scent, while wet earwax tends to smell stronger. Environmental factors can alter this odor, and unusual smells may signal health issues, like infections or metabolic conditions. Fruity or foul smells could indicate serious concerns that you shouldn't ignore. Maintaining ear hygiene can help keep the smell normal. Want to know more about what earwax smells really mean and how to care for your ears? There's plenty to uncover about this fascinating topic!
Key Takeaways
- Healthy earwax typically has a slightly sweet or musty smell, influenced by genetics and ethnic background.
- Wet earwax tends to have a stronger odor than dry earwax, which can indicate underlying health issues.
- Unpleasant odors, such as fruity or foul scents, may signal infections, metabolic disorders, or other health concerns.
- Environmental factors and pollutants can alter earwax smell, making regular ear hygiene essential for monitoring health.
- Regular ear cleaning and maintenance can help maintain normal earwax odor and prevent potential health issues.
Understanding Earwax Composition

Earwax, or cerumen, is primarily produced in the outer third of your ear canal, thanks to a combination of glands and secretions. The sebaceous glands and modified apocrine sweat glands play key roles in this process, alongside ceruminous glands and keratinocytes. As these glands function, they incorporate hair and dead skin cells into the earwax, creating a complex mixture that serves multiple purposes.
The chemical composition of earwax is quite interesting. It includes both saturated and unsaturated long-chain fatty acids, which help form a protective layer against water and foreign particles. You'll also find alcohols like lactic acid and isopropanol, which act as natural antimicrobial agents to fend off infections. Squalene, a natural oil, contributes to the moisturizing properties, while cholesterol helps maintain the consistency of earwax.
This unique blend provides essential protection for the skin lining your ear canal, assisting in cleaning and lubrication. By understanding the composition of earwax, you can appreciate its vital functions in keeping your ears healthy and free from unwanted contaminants.
Types of Earwax Explained
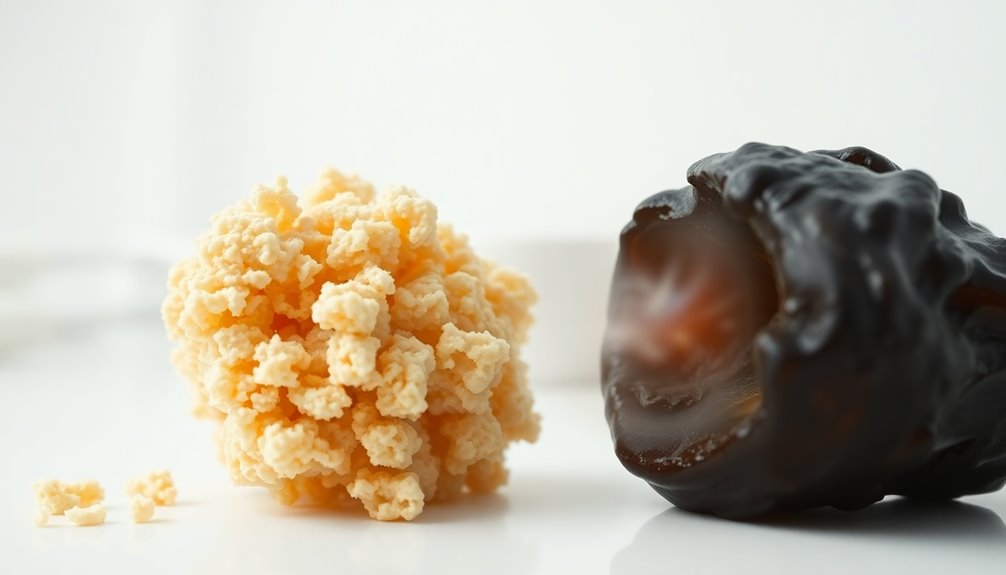

Understanding the composition of earwax lays the groundwork for recognizing its various types, which can differ significantly in consistency and color. The two main categories are wet and dry earwax. Wet earwax typically appears soft and yellow, indicating healthy production. It's common among individuals with one or two copies of the C variant of the ABCC11 gene. This type has a sticky texture due to higher fat content and is more prevalent in Caucasian and African populations.
On the other hand, dry earwax is crumbly, gray to tan, and tends to be less fatty. If you have two copies of the T variant of the ABCC11 gene, you're likely to have this type. Dry earwax is more common among Native Americans and East Asians. Genetic background influences ear wax type, making it essential to understand your own genetics for better ear health.
You might also encounter variations like firm brown earwax, which suggests older, hardened wax, or even runny wax that can appear after swimming. If you notice unusual types or consistency, it's essential to consult a healthcare professional to rule out any underlying issues. Recognizing these differences can help you understand your ear health better.
Normal Earwax Odor
With a slightly sweet or musty aroma, normal earwax odor plays a crucial role in indicating ear health. This subtle scent suggests that your earwax is effectively doing its job of keeping your ears clean and healthy. Most people might not even notice this smell, as it's typically very mild and not bothersome at all.
The musty or sweet odor is linked to the normal functioning of your ear's defense mechanisms, trapping dust, bacteria, and small objects to protect your delicate ear canal. Interestingly, genetic and ethnic differences can influence the smell of earwax. For instance, white men tend to produce more volatile organic compounds in their earwax compared to East Asian men, affecting the overall odor. Additionally, the presence of dead skin cells in earwax contributes to its unique composition and scent.
Keep in mind that while normal earwax odor indicates healthy ear function, changes in smell can occur if earwax isn't drained properly. Regular ear cleaning can help maintain that pleasant, normal odor, ensuring your earwax continues to serve its protective role. The combination of sweat, sebaceous gland secretions, and dead skin cells contributes to this unique scent profile, reinforcing the importance of proper ear hygiene.
Signs of Abnormal Smells
Abnormal smells in earwax can signal underlying health issues that you shouldn't ignore. You might notice changes in the odor of your earwax, which can stem from various factors. For example, genetic differences linked to your race influence the type and smell of your earwax. Wet-type earwax, often found in Caucasians and Africans, tends to have a stronger odor compared to the lighter, flakier dry-type found in East Asians.
Environmental and lifestyle factors also play a role. Exposure to pollutants, chemicals, or a change in diet may alter your earwax's smell. Infections or inflammation in your ears can produce distinctly unpleasant odors, while certain medical conditions, like hormonal disturbances, can affect earwax secretion. Additionally, taste abnormalities can sometimes accompany changes in earwax odor, indicating a broader health issue that may need attention.
If your earwax starts to smell unusual, it may be a sign of something more serious. Identifying these changes early can help you address possible health concerns before other symptoms arise. By paying attention to the smell of your earwax, you can gain valuable insights into your overall health and well-being.
Health Issues Indicated by Smell

Changes in the smell of your earwax could be more than just a minor nuisance; they might indicate underlying health issues that deserve your attention. For instance, if your earwax takes on a fruity scent, it could signal diabetic ketoacidosis, a serious condition linked to elevated acetone levels. On the other hand, a foul smell might point to bacterial infections, such as skin infections that emit a putrid odor or respiratory infections causing persistent bad breath.
If you notice a musty or garlic-like smell, it may suggest liver disease, while an ammonia-like odor could indicate kidney failure. You should also be wary of changes tied to metabolic issues; diabetes can produce breath that smells like rotten apples if not well-managed. Furthermore, gastrointestinal problems, like lactose intolerance, can lead to particularly smelly gas after consuming dairy. If your body odor intensifies following an illness, it might hint at an immune response, as humans can detect illness through changes in body odor. In rare cases, certain cancers can emit specific odors detectable by trained dogs. If you suspect your earwax odor may be linked to these health concerns, it's crucial to consult a healthcare professional.
Factors Influencing Earwax Odor

The odor of your earwax can be influenced by various factors that range from medical conditions to personal hygiene. Infections like swimmer's ear or ear infections can lead to a foul smell due to bacteria or viruses. Conditions such as cholesteatoma or even rarely, ear cancer, can also contribute to unpleasant odors.
Blockages play a significant role too. Excessive earwax buildup, foreign objects stuck in your ear, or impacted wax can all create a smelly situation. When your ear canal is blocked, normal drainage is hindered, leading to odor. Excessive moisture may also promote bacterial growth, which further exacerbates the issue.
Environmental factors and personal hygiene matter as well. If you don't clean your ears regularly, you may find that your earwax starts to smell. Improper use of earwax removal kits can push wax deeper, causing blockages. Additionally, exposure to moisture, dust, and even hair products can add to the unpleasant scent.
Finally, the biological composition of earwax itself can lead to odors. Bacteria breaking down sweat and dead skin cells create foul smells, while volatile organic compounds can vary from person to person. All these factors contribute to the unique scent of your earwax.
Ethnic Variations in Earwax

Earwax varies significantly among different ethnic groups, reflecting a fascinating interplay of genetics and evolution. The type of earwax you have is primarily determined by the ABCC11 gene. If you carry the AA genotype, you'll likely have dry, flaky earwax, while those with the GA or GG genotypes tend to have wet, sticky earwax. This genetic variation originated in northeastern Asia around 2,000 generations ago and influences the lipid content and texture of your earwax.
Wet earwax is common in individuals of African and European descent, while dry earwax is prevalent among East Asians, including Chinese, Koreans, and Japanese. Interestingly, Native Americans and Pacific Islanders show a mixed distribution of both types. As you move from East Asia towards Europe and Africa, the frequency of the dry earwax allele decreases. In fact, it's found in only about 10-20% of Europeans and is virtually absent in African populations. Understanding the ABCC11 gene provides insight into how these genetic variations might impact health conditions, including risks associated with breast cancer.
These variations likely stem from evolutionary advantages conferred by different climates. For instance, dry earwax may have helped keep individuals in colder regions healthier, while wet earwax could pose risks in hot, humid environments.
Maintenance and Hygiene Tips

Maintaining ear health is crucial for preventing discomfort and ensuring proper hearing. Start by using ear drops to soften earwax, which lets your body naturally remove it. Tilt your head toward the ceiling and apply a few drops into your ear canal, holding that position for 3-4 minutes. Repeat this on the other ear, doing it twice a day for 4-5 days for the best results. Look for water-based ear drops with ingredients like hydrogen peroxide or sodium bicarbonate, or opt for oil-based alternatives like olive oil.
For excess earwax, consider ear irrigation with a rubber bulb syringe to flush it out with water or saline. However, always have a professional perform this to avoid damaging your ear. Avoid harmful practices, like using cotton swabs or foreign objects, as they can push wax further in or cause injury. Ears have a natural self-cleaning ability, which can be disrupted by regular cleaning, so it's important to be cautious.
In your daily hygiene routine, gently wipe the outer ear with a soft, dry cloth after showers. If you notice symptoms like ear pain or hearing loss, seek medical attention promptly to prevent complications. Following these tips can help maintain your ear health effectively.
The Role of Earwax in Health

Playing a crucial role in ear health, earwax serves multiple protective functions that go beyond just keeping the ear canal clean. It acts as a filter, preventing harmful objects like bugs, dirt, and sand from reaching your eardrum. Additionally, it contains antimicrobial substances that help guard against infections, trapping dead skin cells and aiding in their removal from your ear. Earwax also serves as a barrier against bacteria and other pathogens, while helping to keep water from entering the ear canal.
Beyond protection, earwax provides lubrication and moisture, preventing dryness and itching. It maintains the health of your ear canal, keeping it from becoming cracked and helping balance its natural pH. Produced by glands in the outer part of the ear canal, it's pushed out through jaw movements, ensuring a self-cleaning process. Furthermore, excessive cleaning can disrupt the natural balance of waxy lubrication in your ears, leading to potential problems.
Your earwax type—wet or dry—can indicate genetic and ethnic differences. Interestingly, earwax can even signal certain health conditions through its smell. So, while it might seem unappealing, earwax plays an essential role in your overall ear health and can provide valuable insights into your body's status.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can Earwax Smell Change Over Time?
Yes, your earwax smell can change over time. Factors like increased sweating after physical activities can lead to a stronger odor. If you develop an ear infection, you might notice a foul smell. As you age, your earwax glands may produce drier wax, which usually doesn't alter the smell. However, if you experience a change in odor, it's important to pay attention to any accompanying symptoms, as they could indicate an underlying issue.
How Often Should I Clean My Ears?
How often you should clean your ears really depends on your individual needs. If you produce excess wax, you might want to schedule cleanings every three months. For others, once a year may be enough. Pay attention to symptoms like muffled hearing, itchiness, or discomfort; these can indicate it's time for a cleaning. Regular maintenance is especially important if you use hearing aids or have a history of ear infections.
Is Earwax Smell Related to Diet?
Yes, earwax smell can definitely be related to your diet. Foods high in sugar, dairy, gluten, and caffeine can increase earwax production and potentially lead to stronger odors. Spicy foods and dehydration can also thicken earwax, making it more prone to unpleasant smells. Staying hydrated and maintaining a balanced diet rich in fruits and vegetables can help keep your earwax healthier and reduce any odors. So, what you eat really matters!
Can Earwax Smell Indicate Dehydration?
You might wonder if earwax smell indicates dehydration. While dehydration can lead to dry skin, it isn't directly linked to earwax odor. The smell primarily stems from the type of earwax you have, bacterial activity, and hygiene practices. Factors like infections or environmental influences play a bigger role in producing odor. So, if you notice an unusual smell, it's wise to consider those factors rather than focusing solely on dehydration.
Does Earwax Smell Differ by Age?
Earwax smell doesn't really differ by age. While older individuals might have drier earwax, the odor itself usually stays consistent. It can vary based on the type of earwax—wet or dry—and individual health conditions. If you notice a strong or foul smell, it could indicate an infection or blockage, regardless of your age. Keeping an eye on your ear health is essential for addressing any potential issues.
Conclusion
In conclusion, earwax can have a normal odor, but any sudden or strong changes in smell might signal health issues. Understanding the factors that influence earwax odor, including ethnicity and hygiene, can help you maintain ear health. Remember, earwax plays a crucial role in protecting your ears, so don't overlook it. If you notice any concerning smells or changes, it's wise to consult a healthcare professional for peace of mind and proper care.